The Exchange of Genetic Material Between Homologous Chromosomes Is Called
The homologous pairs then separate each pair being pulled to opposite ends. The consequences of each crossover event.
What Is The Exchange Of Genetic Material Between Two Homologous Chromosomes Quora
In this process the genetic information is rearranged between chromosomes that possess similar sequences.
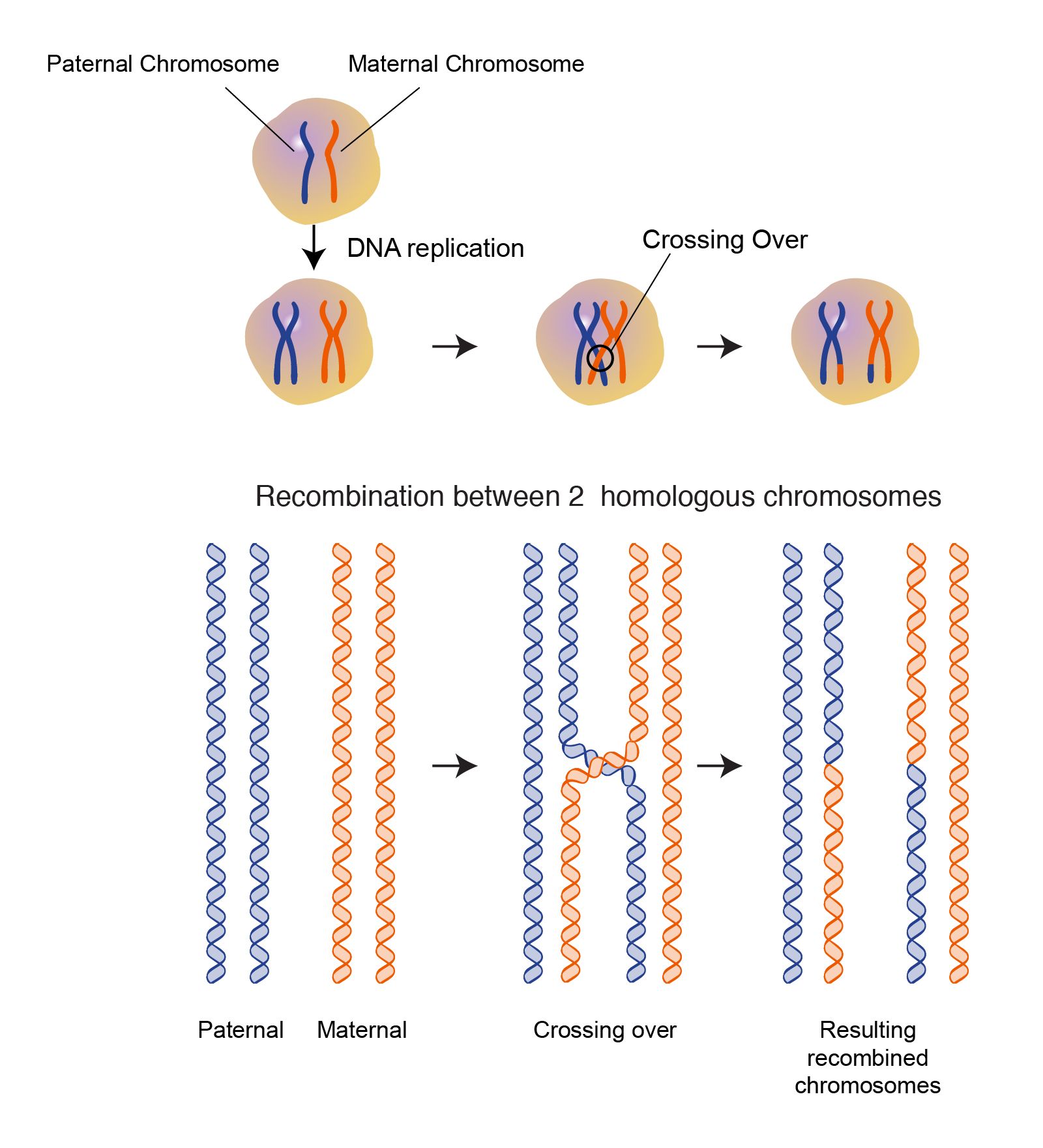
. These exchanges take place at sites called chiasmata which bind the chromosomes until all the recombination events are finished at that location. Its two steps such as prophase-1 and prophase-2. The G1 phase occurs immediately after cell division and is a period of recovery for the cell.
Exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes only occurs during Prophase I of meiosis. Homologous pairs of chromosomes are separated and pulled to opposite poles of the cell and the spindle. Homologous chromosomes replicate by forming identical copies of chromosomes called sister chromatids.
During S phase all the DNA in the cell is duplicated but without any genetic exchange. Actual pieces of one of the sister chromatids break off and reattach to the other homolog. If both resulting hybrid or derivative chromosomes carry one centromere.
In synapsis the genes on the chromatids of the homologous chromosomes are aligned precisely with each other. If single breaks occur in two separate chromosomes incorrect joining of the resulting fragments may lead to the exchange of material between chromosomes translocation. Each pair of chromosomescalled a tetrad or a bivalentconsists of four chromatids.
Also during this stage the homologous chromosomes exchange some of their genetic material in a process called recombination. On the other hand during mitotic prophase the chromosomes condense. Each chromosome has two sister chromatids each of which contains a duplex DNA.
Chromosomes may become coiled around each other and their chromatids may remain in contact at points called chiasmata. At this point the homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material by the process of crossing over see linkage group. During chromosomal crossing-over the DNA double helix is broken in both a maternal chromatid and a homologous paternal chromatid so as to exchange fragments between the two nonsister chromatids in a reciprocal fashion by a process known as genetic recombination.
Part exchange occurs which changes the gene arrangement of the chromosomes. The synaptonemal complex supports the exchange of chromosomal segments between non-sister homologous chromatids a process called crossing over. The resulting daughter cells are four and already haploid.
The homologous chromosomes segregate during meiosis I whereas the sister chromatids during meiosis II. The homologous chromosomes one maternal and the other. In eukaryotes genetic recombination during meiosis can lead to a novel set of genetic information that can be passed on from the parents to the.
This exchange is called crossing over. After crossing over the sister chromatids for each chromosome are no longer identical to one. The molecular details of this process are discussed in Chapter 5.
This genetic recombination is what produces the variation of genes. This process is generally mediated by homology. A process called crossing over can happen during prophase I.
Translocation mutation between non-homologous chromosomes is not to be confused with crossover between homologous chromosomes or regions of chromosomes. This is when homologous chromosomes overlap and exchange genetic material. Nuclear membrane disappears completely making the chromosomes free in the cytoplasm.
Crossing over can be observed. Deletion the loss of genetic material and duplication the over-copying of. Next each pair of homologous chromosomes undergoes synapsis to form a complex involving two pairs of sister chromatids.
Homologous pairs of chromosomes line up along the equator of the cell Anaphase 1. DNA recombination involves the exchange of genetic material either between multiple chromosomes or between different regions of the same chromosome. Different parts of the homologous chromosomes will cross over and exchange certain chunks of genetic material.
During synapsis homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material between one another. This event is called recombination or more commonly crossing over. In a balanced reciprocal translocation DNA from two different chromosomes is exchanged without net loss.
The tight pairing of the homologous chromosomes is called synapsis. Homologous paternal and maternal chromosomes pair up along the midline of the cell. Chromosomal crossover or crossing over is the exchange of genetic material during sexual reproduction between two homologous chromosomes non-sister chromatids that results in recombinant chromosomesIt is one of the final phases of genetic recombination which occurs in the pachytene stage of prophase I of meiosis during a process called synapsis.
The purpose of crossing over is to further increase genetic diversity since alleles for those genes are now on. Homologous genetic recombination occurs in eukaryotes at the time of gamete formation during long prophase I of meiosis. In late prophase chiasmata are formed points where the DNA from non-sister chromatids crosses over resulting in the exchange of genetic material.
Crossing-over is the process that can give rise to genetic recombination. The duplicated homologous chromosomes pair and crossing-over occur. Genetic recombination also known as genetic reshuffling is the exchange of genetic material between different organisms which leads to production of offspring with combinations of traits that differ from those found in either parent.
The nucleolus disappears during prophase I. Chromosomal material is exchanged between the two pairs of sister chromatids.

Crossing Over The Exchange Of Genetic Material Between Homologous Chromosomes That Results In Recombinant Chromosomes I Chromosome Genetics Williams Syndrome

0 Response to "The Exchange of Genetic Material Between Homologous Chromosomes Is Called"
Post a Comment